Paper category: Original research paper
Corresponding author: Elena V. Anufriieva (lena_anufriieva@mail.ru)
DOI: 10.1515/ohs-2018-0021
Received: December 19, 2017
Accepted: February 27, 2018
Full text: here
Citation (APA style):
Abstract
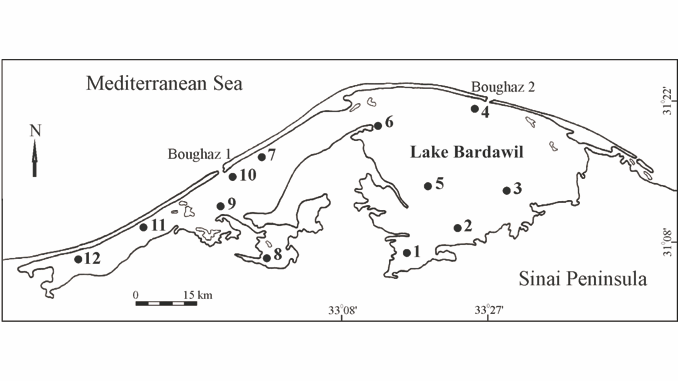
Coastal Lake Bardawil (Egypt) is one of the largest hypersaline lakes in the world. In 2009–2010, the authors studied composition, distribution and seasonal dynamics of copepods at 12 sites.
A total of 10 species of copepods were recorded in zooplankton during the study period, including 5 Calanoida, 2 Cyclopoida and 3 Harpacticoida. Oithona nana was the most common and most abundant species. All copepods in the lake can be divided into three groups: 1) planktic species that form stable populations, 2) species of Mediterranean plankton incidentally entering the lake from the adjacent sea area, 3) benthic Cyclopoida and Harpacticoida that can be abundant in plankton. Two species – Acartia tonsa and A. danae were recorded here for the first time. The total abundance of copepods in the lake was significantly higher (90 times on average) compared to that observed in 2008–2009 in the waters of the Egyptian Mediterranean Sea. Since 1967, the complex of common and dominant copepod species in the lake has changed significantly. The total average annual copepod abundance varied: in 2002 – it was about 4000 ind. m−3, in 2004 – 152 000 ind. m−3, in 2005 – about 25 300 ind. m−3, and in 2009–2010 – about 56 000 ind. m−3.


Bądź pierwszy, który skomentuje ten wpis