Paper category: Original research paper
Corresponding author: Xiaohui Chen (xhchenffri@hotmail.com)
DOI: 10.1515/ohs-2018-0011
Received: June 05, 2017
Accepted: October 20, 2017
Full text: here
Citation (APA style):
Abstract
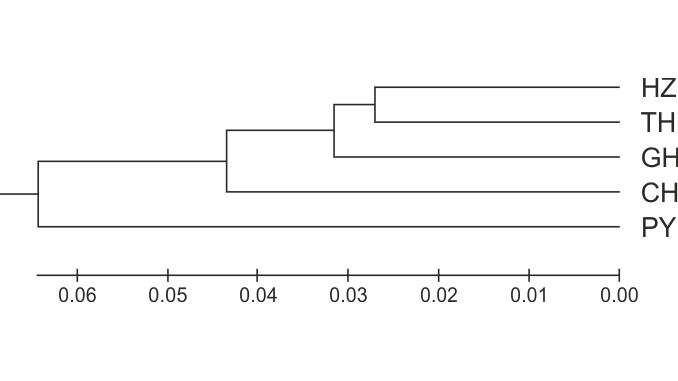
Yellow catfish, Pelteobagrus fulvidraco, is an important commercial freshwater species in China. Knowledge about the genetic diversity of the yellow catfish is important to support the management and conservation programs, which would subsequently support the sustainable production of this species. To investigate the genetic diversity and the structure of yellow catfish in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, 125 individuals from five lakes were genotyped using 13 microsatellite markers. Moderate genetic diversity was determined in all populations, with the observed heterozygosity (HO) ranging from 0.42 to 0.49 and the expected heterozygosity (HE) ranging from 0.51 to 0.61. Low to moderate genetic differentiation among the populations was revealed from pairwise FST values (p < 0.05), as well as from analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA). The UPGMA dendrogram and Bayesian clustering analysis indicated a correlation between genetic differences and geographic distance – four populations from the lower reaches clustered together, whereas the Poyang Lake (PY) population formed a separate cluster. The present study would be helpful in the wild stock management and artificial propagation programs for yellow catfish in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River.

Bądź pierwszy, który skomentuje ten wpis